Augmented Reality (AR), Virtual Reality (VR), and Mixed Reality (MR) are increasingly being integrated into healthcare applications, transforming various aspects of medical practice, education, and patient care. Below are some key areas where these technologies are making significant impacts.
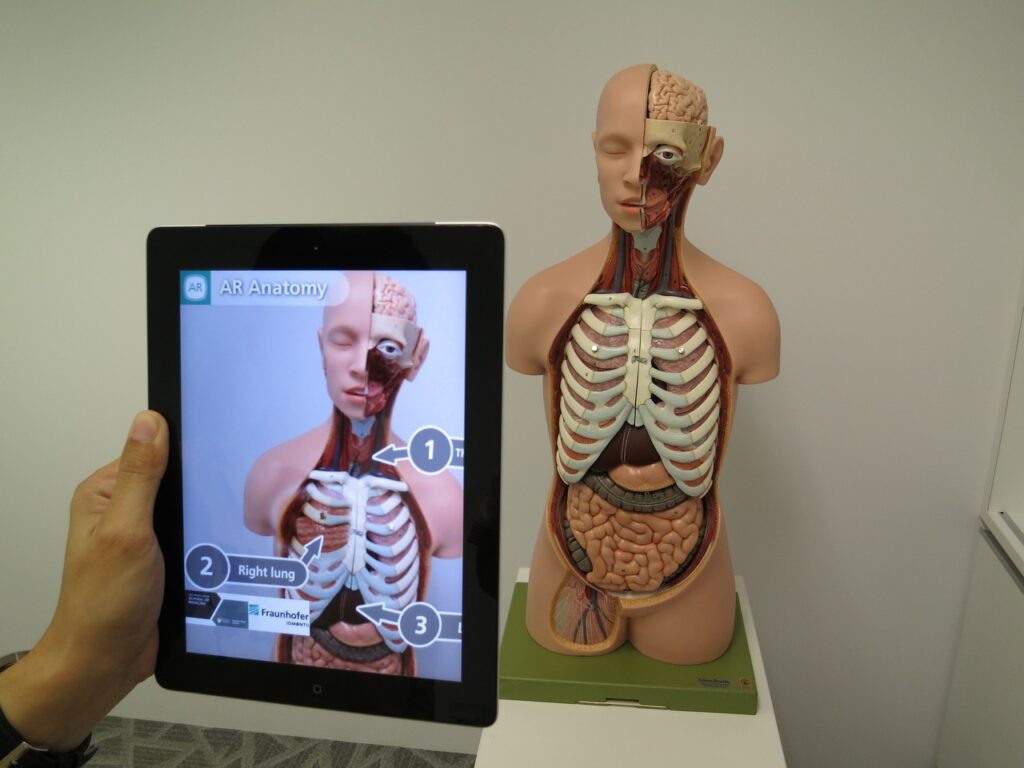
Surgical Assistance and Planning
AR for Surgical Visualization: Surgeons can use AR to overlay digital images of a patient’s anatomy onto their physical body during procedures. This enhances precision by allowing them to visualize internal structures such as organs and veins in real-time, improving surgical outcomes and reducing risks.
VR Surgical Training: VR provides immersive simulations for surgical training, allowing medical professionals to practice techniques in a safe environment. This method enhances skill acquisition without the immediate pressures of real-life surgeries.
Medical Education
Interactive Learning: Both AR and VR facilitate interactive medical education by allowing students to explore 3D models of human anatomy. For instance, the HoloAnatomy app used with Microsoft’s HoloLens enables students to visualize complex structures dynamically.
Enhanced Engagement: These technologies increase student engagement and retention of knowledge by providing hands-on experiences that traditional methods cannot offer, such as repeated practice with anatomical specimens.
Patient Care and Rehabilitation
Physical Therapy: AR applications can guide patients through rehabilitation exercises by overlaying instructions onto their real-world environment. For example, systems like Bionik’s AR-powered rehabilitation system help stroke patients regain mobility through interactive exercises.
Mental Health Treatment: VR is utilized for therapeutic purposes, such as treating anxiety, PTSD, and phobias by immersing patients in controlled environments that simulate their fears or stressors.
Remote Consultations and Collaboration
Telemedicine: AR enables remote consultations where specialists can guide less experienced doctors through procedures using real-time visual aids. This fosters collaboration without geographical limitations.
Patient Education: AR applications help patients understand their conditions better by visualizing complex medical information, such as tumors or treatment effects, which can enhance compliance with treatment plans.
Medical Equipment Maintenance
AR for Equipment Guidance: AR technology assists in the maintenance and repair of medical devices by providing technicians with real-time guidance on procedures, thereby reducing downtime and ensuring
equipment reliability.
Enhanced Diagnostic Processes
Improved Imaging Techniques: AR can overlay diagnostic images (like MRIs or CT scans) onto a patient’s body during examinations, helping doctors identify abnormalities more effectively.
Emergency Situations
Real-Time Assistance: Applications can assist first responders by displaying critical information about patients or the location of emergency equipment (like defibrillators) in real-time.
Conclusion
The integration of AR, VR, and MR technologies in healthtech is revolutionizing how medical professionals train, diagnose, treat patients, and manage healthcare operations. As these technologies continue to evolve, their potential to enhance patient outcomes and streamline healthcare processes will likely expand even further.

Sources
https://omnivatelehealth.com/blog/ar-in-healthcare/
https://www.onirix.com/ar-vs-mr/
https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/top-applications-augmented-reality-ar-healthcare-jeffrey-boopathy/












