Radiology involves various imaging techniques used to visualize the internal structures of the body for diagnosis and treatment. The most common radiological imaging methods include X-ray, CT (computed tomography), and MRI (magnetic resonance imaging).
Here some distinct characteristics of the Radiolgy types :
X-ray
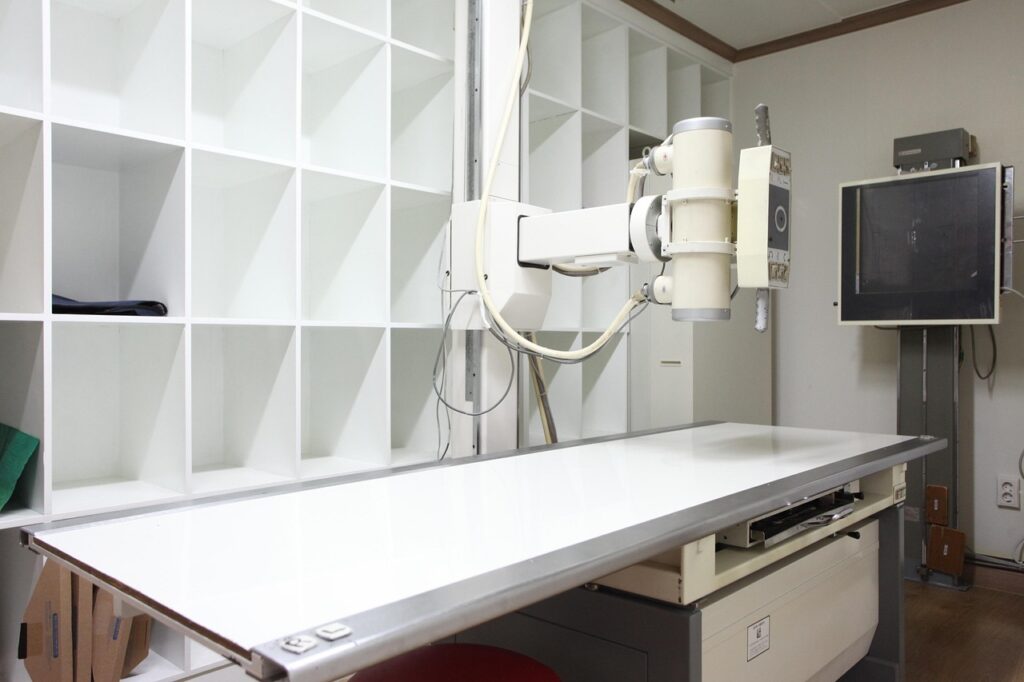

Uses ionizing radiation to produce 2D images of the body, Dense structures like bones and teeth block the radiation and appear white on the image, while soft tissues appear gray or black. It is fast, widely available, and often the first imaging test used. Best suited for detecting fractures, dislocations, bone deformities, and some diseases affecting bones. Cannot effectively show soft tissue injuries or subtle bone damage like hairline fractures.
CT Scan
Also uses ionizing radiation but provides detailed cross-sectional (3D) images by taking multiple X-ray images from different angles. Offers higher detail than X-rays, especially for bones, organs, and blood vessels. Often used in emergency settings for trauma, suspected fractures, organ injuries, and complex conditions. Can use contrast dyes to enhance visualization of certain structures. Faster than MRI but less effective than MRI for soft tissue visualization.
MRI
Does not use ionizing radiation; instead, it uses strong magnetic fields and radio waves to generate images. Provides highly detailed images of both hard and soft tissues, including muscles, ligaments, tendons, brain, spinal cord, and internal organs. Ideal for diagnosing soft tissue injuries, inflammation, herniated discs, and joint problems. Takes longer than X-rays or CT scans and is less widely available. Loud during operation and contraindicated for patients with certain metal implants.
Summary Table & Summary
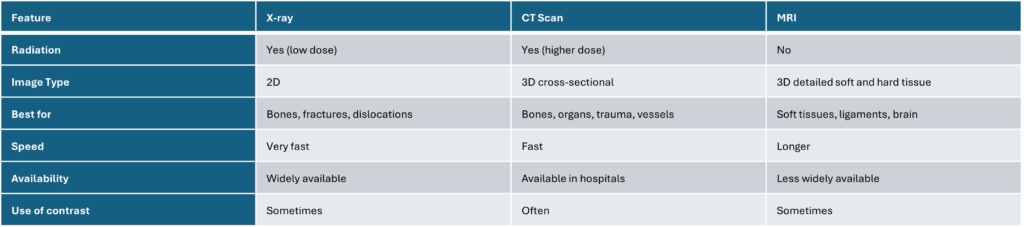
Radiology as a field includes these imaging modalities and others, used by radiologists to diagnose and sometimes treat diseases through imaging guidance.
In essence, X-rays are quick and good for bone injuries, CT scans provide more detailed images for complex cases, and MRIs offer the best detail for soft tissues without radiation exposure.
The choice depends on the clinical situation and the body part being examined.
And now: Advances in radiology 2025
Modalities such as CT (Computed Tomography), MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging), and Roentgen (X-ray) are characterized by several cutting-edge developments:
Artificial Intelligence (AI) Integration
AI is revolutionizing diagnostic imaging by enabling faster, more accurate image analysis and anomaly detection.
AI algorithms assist radiologists in detecting subtle patterns missed by the human eye, reducing diagnostic errors, and generating preliminary reports automatically.
For example, AI stroke detection algorithms now achieve near 99% sensitivity, significantly speeding emergency diagnosis.
Enhanced Imaging Modalities
4D Imaging: Advances in 4D imaging allow real-time visualization of dynamic physiological processes, such as blood flow in cardiac MRI or fetal movements in ultrasound, improving diagnostic precision.
Photon-Counting CT (PCCT): This new CT technology offers higher resolution images at lower radiation doses and can distinguish multiple contrast agents simultaneously, improving tissue characterization and reducing repeat scans.
Hybrid Imaging: PET-MRI systems combine functional and anatomical data, enhancing cancer detection and reducing false negatives in biopsies.
Portable and Mobile Imaging
Portable and handheld imaging devices are increasingly adopted, expanding access to advanced diagnostics in emergency, rural, and underserved settings. Innovations like helium-free MRI machines make mobile imaging more practical and energy-efficient.
Predictive Analytics and Personalized Medicine
AI-powered predictive models analyze imaging data over time to forecast disease progression, such as multiple sclerosis or cardiac events, enabling proactive care and personalized treatment planning.
Improved Workflow and Accessibility
Cloud-based imaging platforms and teleradiology facilitate remote image analysis and reporting, improving access to expert radiology services worldwide, especially in underserved regions.
Summary Table: Key Advances in Radiology (CT, MRI, Roentgen) in 2025

These innovations collectively enhance early disease detection, diagnostic accuracy, patient outcomes, and healthcare accessibility while addressing challenges like radiologist shortages and sustainability.
SOURCES
https://www.envrad.com/difference-between-x-ray-ct-scan-and-mri/
https://www.hopkinsmedicine.org/health/treatment-tests-and-therapies/ct-vs-mri-vs-xray
https://www.premierortho.org/the-difference-between-x-ray-ct-and-mri
https://northcentralsurgical.com/whats-the-difference-between-an-x-ray-ct-scan-and-mri/
https://www.kenhub.com/en/library/anatomy/medical-imaging-and-radiological-anatomy
https://orthoinfo.aaos.org/en/treatment/x-rays-ct-scans-and-mris
https://www.healthimages.com/what-is-radiology/
https://onestepdiagnostic.com/what-is-the-difference-between-radiology-and-medical-imaging/
https://www.uscimaging.com/blog/the-top-trends-in-diagnostic-imaging-for-2025/
https://blog.medicai.io/en/future-of-medical-imaging/
https://sharedimaging.com/2025trends
https://openmedscience.com/vision-2025-transforming-healthcare-through-the-future-of-medical-imaging
https://gcgglobalhealthcare.com/key-medical-imaging-trends-to-watch-in-2025












