Digital health includes digital care programs and technologies for health, healthcare, living, and society. It enhances the efficiency of healthcare delivery and to make medicine more personalized and precise.
It uses information and communication technologies to facilitate understanding of health problems and challenges faced by people receiving medical treatment and social prescribing in more personalised and precise ways.
Worldwide adoption of electronic medical records has been on the rise since 1990 and is closely correlated with the existence of universal health care.
Generally, digital health interconnects health systems to improve the use of computational technologies, smart devices, computational analysis techniques, and communication media to aid healthcare professionals and their patients manage illnesses and health risks, as well as promote health and wellbeing.
Digital health technologies include:
- Hardware
- Software solutions
- Services
- Telemedicine
- Wearable devices
- Augmented reality
- Virtual reality
Although digital health platforms enable rapid and inexpensive communications, critics warn against potential privacy violations of personal health data and the role digital health could play in increasing the health and digital divide between social majority and minority groups, possibly leading to mistrust and hesitancy to use digital health systems.
Digital Health Elements
The prominence of Digital health in the past century has culminated for the emergence of three reasons:
Primary Care Services
The first group of these services is known as primary care services in the domain of digital health. These services include wireless medical devices that utilize technology such as Wi-Fi or Bluetooth, as well as applications on mobile devices that encourage the betterment of an individual’s health as well as applications that promote overall general wellness.
Acute Care Services
The second group of these services is known as acute care in the digital health domain. These services include telemedicine which is defined as handling patients over some sort of streaming device and is targeted towards areas where the population is more widely scattered, medical devices that incorporate different aspects of software otherwise known as SaMD, and examples of these devices are pacemakers.
Digital Health Information solutions and Applications
The rest of the elements of Digital health that do not fall so squarely into acute or primary care services are listed as the transmission of medical education and information between practitioners and researchers through the utilization of digital technologies and applications that can be employed by doctors for risk-assessment regarding patients.
Devices that can be utilized for the improvement and management of bodily purposes as well as the encouragement of the education of digital health to the public.
There are also patient-based applications that can be utilized to share information by individual patients as well as encourage the usage of drug trials. The tracking of outbreaks of disease by the use of mass media that social media has developed has also come about through Digital Health.
Finally the recording of the environment around sensor devices that are being utilized for the betterment of the community.
Technologies
Digital health technologies come in many different forms and extend into various parts of healthcare. As new technologies develop, digital health, as a field, respectively transforms.
In fact some of these technologies are being propelled by the startup space, which has been followed via Internet or online media sources such as podcasts on digital health entrepreneurs.
The National Institute for Health and Care Research (NIHR) has published a review of research on how digital health technologies can help manage health conditions.
One of the Technology areas is Internet of Medical Things (IOMT)
The Internet of Medical Things (IOMT) is the network of Internet-connected medical devices, hardware infrastructure, and software applications used to connect healthcare information technology.
Due to several stakeholders the IOMT solutions have to serve multiple Users and Interest groups with different knowledge and skills.
Therefore these solutions have to be shaped carefully in usability, security and safety and according Medical Device Regulations (MDR) or US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) classifications and some, depending on classification level, have to be approved by clinical trial results.
Here a short check list of the main User Impact areas:
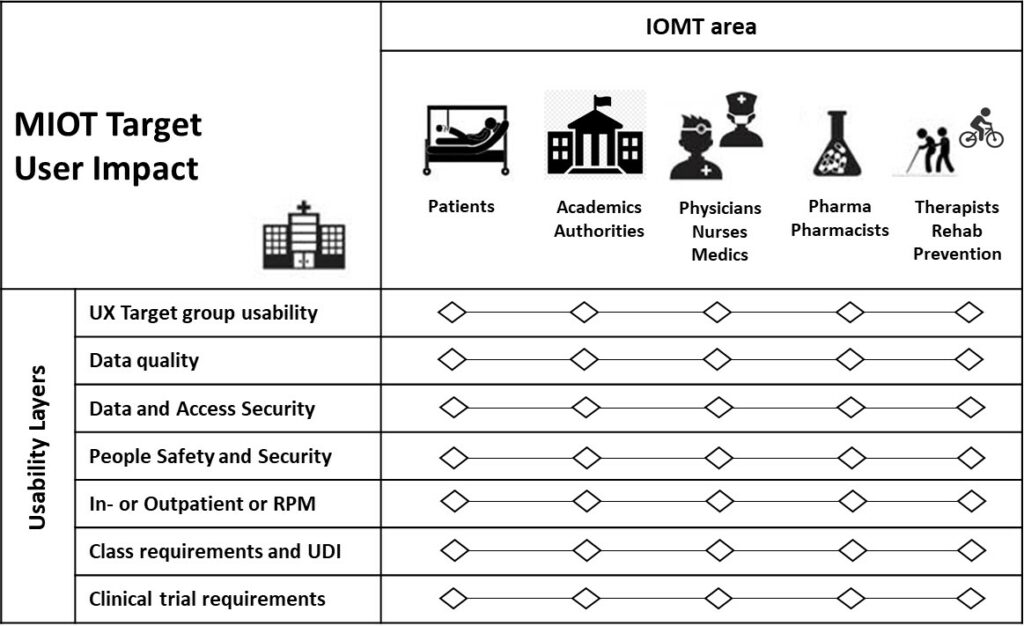
Many of the most innovative digital Health ideas products are based on IOMT Technology.
Many new ideas are challenging and start-ups with many aspects of monetisation, market impact, user impact, value add, and how to apply the findings to this idea and the technology properly.
Here some check points for the entrepreneurs of IOMT digital Health solutions:
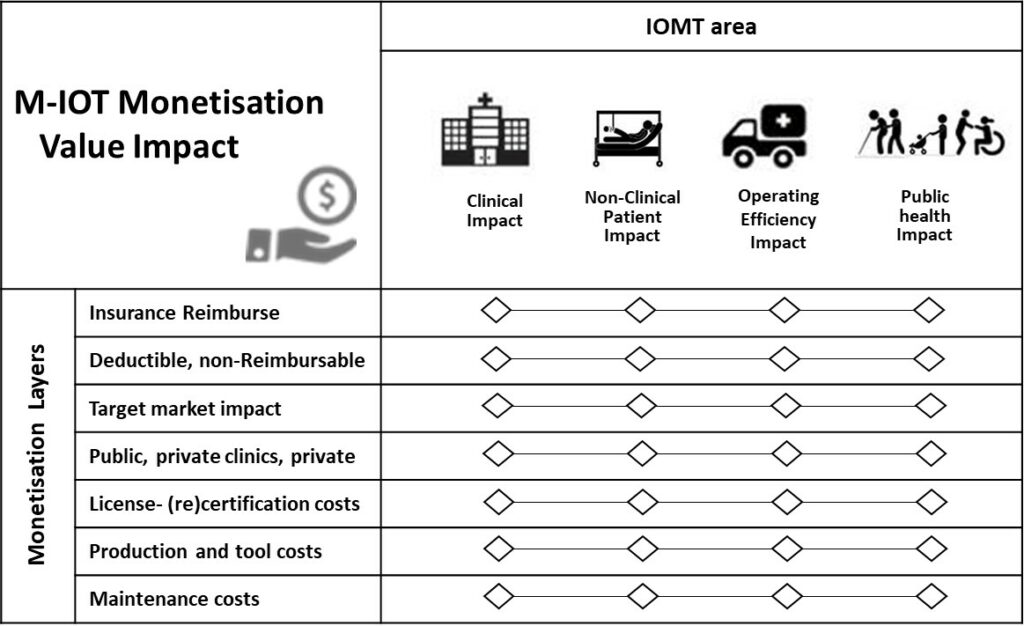
One example of the IOMT Technology based Digital Health Applications is Telemedicine
Telemedicine is one of the broadest areas of digital health. It encompasses the digitization of medical records, remote care, appointment booking, self-symptom checkers, patient outcome reporting, and many others.
Digital and remote clinics are commonly used to provide quick, nonurgent consultations that save both the patients and doctors time. Especially with the COVID-19 pandemic, this type of treatment has become the primary way doctors are seeing their patients and may be as effective as face to face appointments.
This type of digital treatment keeps both parties safe and is a reliable method that physicians plan to use for routine checks even after the pandemic ends.
Another example of IOMT in digital Health are Wearables
Wearable technology comes in many forms, including smartwatches and on-body sensors. Smartwatches were one of the first wearable devices that promoted self-monitoring and were typically associated with fitness tracking.
Many record health-related data, such as “body mass index, calories burnt, heart rate, physical activity patterns”.
Beyond smartwatches, researchers are developing smart-related bodywear, like patches, clothes, and accessories, to administer “on-demand drug release”.
This technology can expand into smart implants for both severe and non-severe medical cases, where doctors will be able to create better, dynamic treatment protocols that would not have been possible without such mobile technology.
These technologies are used to gather data on patients at all times during the day. Since doctors no longer need to have their patients come into the office to collect the necessary data, the data can lead to better treatment plans and patient monitoring. Doctors will have better knowledge into how well a certain medication is performing. They will also be able to continuously learn from this data and improve upon their original treatment plans to intervene when needed.
Digital Health innovations combining Augmented-, Virtual Reality and IOMT Technology
IOMT Technology combines many different sensors, connects devices and delivers data and streams videos to central health care observation and safety points e.g. for Remote Patient Monitoring and Remote Patient Management (RPM).
As well the provision of rehabilitation programs, trainings and also patients condition check makes IOMT Tech possible.
Augmented Reality
In digital health, augmented reality technology enhances real-world experiences with computerized sensory information and is used to build smart devices for healthcare professionals.
Since the majority of patient-related information now comes from hand-held devices, smart glasses provide a new, hands-free augmented way for a doctor to view their patient’s medical history.
The applications of this technology can extend into data-driven diagnosis, augmented patient documentation, or even enhanced treatment plans, all by wearing a pair of smart glasses when treating a patient.
Virtual Reality
Another similar technology space is virtual reality, which creates interactive simulations that mimic real-life scenarios and can be tailored for personalized treatments.
Many stroke victims lose range of motion and under standard treatment protocols, Other patients have long-term upper muscular dysfunction, as the lower body is primarily targeted during therapy.
Repeated actions and the length of therapy are the two main factors that show positive progress towards recovery. Virtual reality technologies can create various 3D environments that are difficult to replace in real-life but are necessary to help patients retrain their motor movements. These simulations can not only target specific body parts, but can also increase in intensity as the patient improves and requires more challenging tasks.
Innovation cycle
The innovation process for digital health is an iterative cycle for technological IOMT solutions that can be classified into five main activity processes from the identification of the healthcare problem, research, digital solution, and evaluating the solution, to implementation in working clinical practices.
Digital health may incorporate methods and tools adopted by software engineering, such as design thinking and agile software development.
These commonly follow a user-cantered approach to design, which are evaluated by subject-matter experts in their daily life using real-world data.
Conclusion
IOMT is an essential building block for many digital Health applications and solutions. New innovative ideas have to be checked and proved carefully. If the right experts combine and integrate MIOT with other Technologies great products are to predict.












