For HealthTech applications, several radio technologies can be compared based on key factors such as range, power consumption, data rate, network topology suitability, and specific medical use cases.
This comparison should guide HealthTech designers in choosing radio technologies tailored to application requirements, environment, data needs, and power constraints.
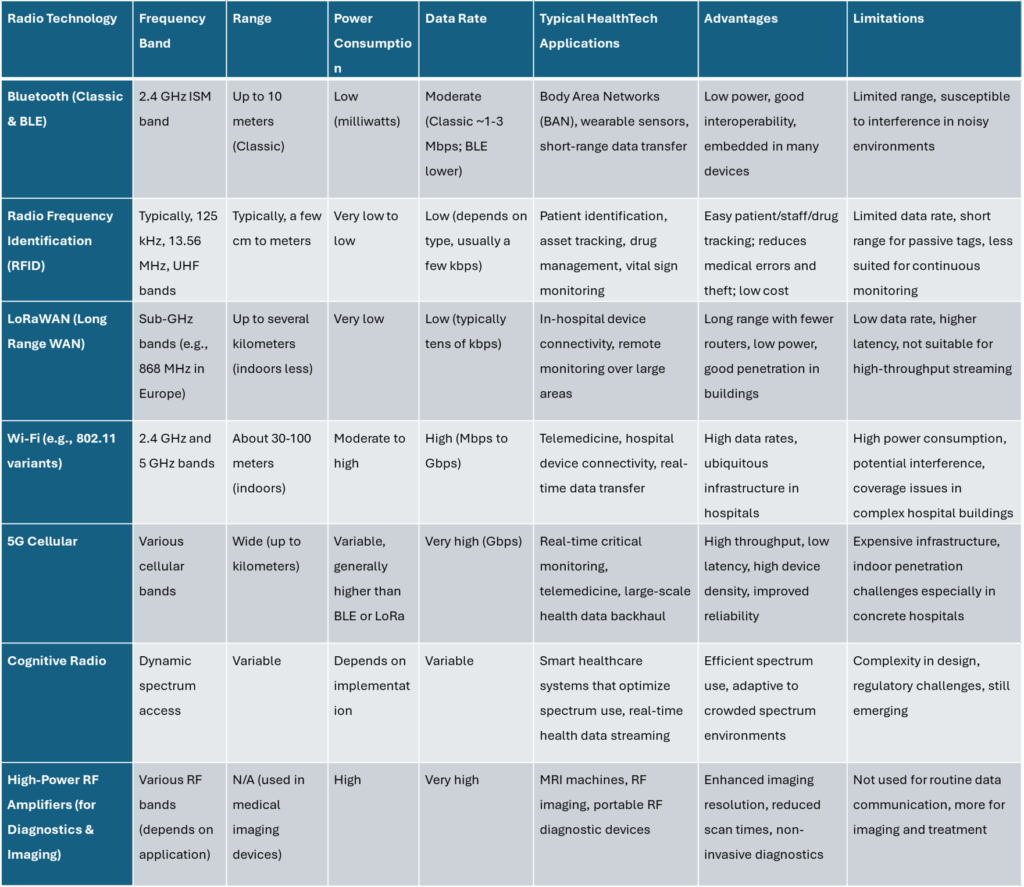
Comparison Table: Radio Technology and HealthTech Applications
Key Insights
Bluetooth
is widely used in wearable devices and personal health networks due to its low power and reasonable data rate over short distances (~10 m), ideal for body area networks with sensors collecting vital signs.
RFID
excels in patient identification, asset tracking, and reducing medical errors. It facilitates drug administration accuracy and staff identification with low cost and power, but data rates and ranges are limited compared to other radios.
LoRaWAN
is gaining traction for in-hospital device connectivity because it requires fewer routers and less installation time with long-range, low-power operations. It is well suited for applications needing wide coverage without high data rates.
Wi-Fi and 5G
provide high data rates essential for complex hospital environments and real-time critical monitoring. However, their power consumption and physical infrastructure challenges such as thick hospital walls and network congestion must be managed carefully.
Cognitive radio technologies
offer promising advances by dynamically managing spectrum resources for healthcare IoT devices, enhancing the reliability of real-time data transmission in crowded spectrum scenarios.
For medical imaging and diagnostics,
specialized high-power RF amplifiers are crucial for MRI and portable diagnostic devices, providing non-invasive and high-resolution imaging beyond typical communication radios.
Summary: Selection depends on specific HealthTech needs
For wearables and body sensors,
Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) is dominant due to its low power and adequate range.
For asset and patient tracking,
RFID is highly effective.
For in-hospital device connectivity over wider areas,
LoRaWAN offers an optimized solution with fewer infrastructure needs.
For high-speed, real-time critical data transfer inside hospitals,
Wi-Fi and emerging 5G networks are preferred but come with complexity and power trade-offs.
For advanced diagnostics and imaging,
high-power RF technologies support precision imaging equipment rather than ongoing data telemetry.
Sources
https://bc.itl.waw.pl/Content/491/JTIT-2005_4_40.pdf
https://www.mi.fu-berlin.de/inf/groups/ag-tech/publications-old/1__resources/terfloth07aal.pdf
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3872592
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9398041
https://encyclopedia.pub/entry/49460
https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/revolutionizing-healthcare-role-rf-technologies-modern-thaware-oyidf












