The fields of Mixed Reality (MR), Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) are rapidly evolving, driven by technological advancements and innovative applications across various sectors. Here are some of the latest developments and something about the main areas of these technologies:
- Overview and Recent Advances in Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR)
- Differences Between Mixed Reality, Augmented Reality, and Virtual Reality
- Haptic feedback in VR
Overview and Recent Advances in Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) and Mixed Reality (MR).
Key Trends in VR and AR
Mixed Reality (MR): This technology blends elements of both AR and VR, allowing for interactive virtual objects to coexist with the real world. MR enhances immersion beyond what traditional AR can offer, creating more engaging experiences.
Retail: AR technologies are revolutionizing shopping experiences by allowing consumers to visualize products in their own environments before purchasing. This capability has been shown to significantly increase consumer confidence and reduce purchase hesitation.
Entertainment: MR, AR and VR are reshaping the entertainment landscape. From immersive gaming experiences to interactive live events, these technologies are creating new ways for audiences to engage with content. For instance, theme parks are incorporating AR to enhance visitor experiences during wait times
MR, VR and AR for Healthcare: The integration of MR, VR and AR into healthcare is transforming various aspects of medical practice, from patient care to medical training. Recent advancements highlight their potential to enhance diagnostics, treatment, and overall patient experiences.
Future Outlook
The future of AR and VR looks promising as both technologies continue to mature. Innovations such as real-time text detection in AR, enhanced object identification, and the development of affordable wearable devices like Apple’s Vision Pro are expected to drive widespread adoption. As these technologies become more integrated into everyday life, we may see a shift toward using AR glasses for tasks traditionally performed on smartphones. In summary, the advancements in VR and AR are not only enhancing user experiences but also transforming various industries by providing innovative solutions that were previously unimaginable.
Differences Between Mixed Reality, Augmented Reality, and Virtual Reality
Understanding the distinctions between Mixed Reality (MR), Augmented Reality (AR), and Virtual Reality (VR) is essential for grasping how these immersive technologies interact with the real world and each other. Here’s a breakdown of each technology:
Definitions
Virtual Reality (VR): This technology immerses users in a fully artificial digital environment, completely replacing the real world. Users typically wear headsets that block out their surroundings, allowing them to interact with a computer-generated space using controllers or hand tracking.
Augmented Reality (AR): AR overlays digital content onto the real world, enhancing the user’s perception of their environment without fully immersing them in a different space. This is commonly experienced through smartphones or AR glasses, where digital elements are superimposed on the physical world.
Mixed Reality (MR): MR combines elements of both AR and VR, allowing users to interact with both real and virtual objects in a shared environment. Unlike AR, MR enables these digital objects to be anchored to the real world, creating a more integrated experience where users can manipulate virtual elements as if they were part of their physical surroundings.
Key Differences
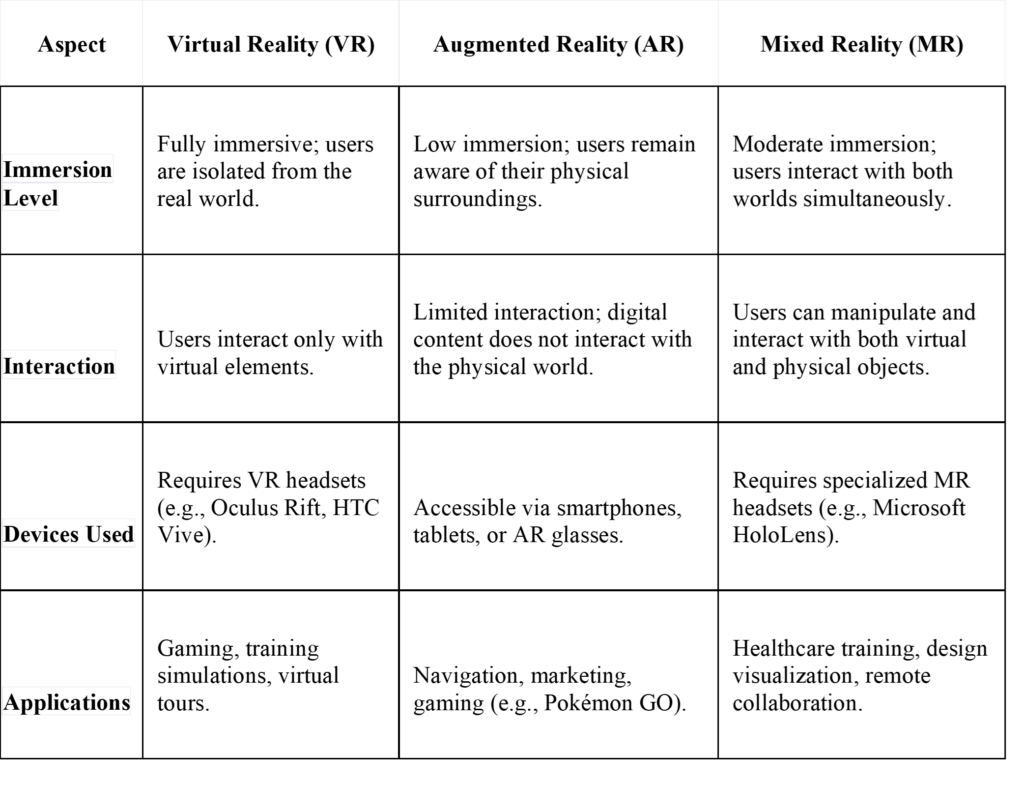
Conclusion
In summary, while all three technologies fall under the broader category of Extended Reality (XR), they serve different purposes and provide varying levels of interaction and immersion. VR offers complete immersion in a digital realm, AR enhances the real world with digital overlays without deep interaction, and MR allows for an interactive blend of both realities where users can engage with virtual objects as if they were part of their physical environment.
What are the main benefits of haptic feedback in VR
Haptic feedback in virtual reality (VR) offers a range of significant benefits that enhance user experience and interaction. Here are the main advantages:
Enhanced Immersion and Realism
Tactile Sensations: Haptic feedback provides users with physical sensations that correspond to virtual actions, making experiences feel more authentic. For instance, users can feel the recoil of a weapon in a game, which adds depth to the experience.
Bridging Digital and Physical Worlds: By simulating touch and movement, haptic feedback helps bridge the gap between the physical and digital environments, allowing users to interact with virtual objects as if they were real.
Improved User Engagement
Increased Satisfaction: Users report higher levels of satisfaction when tactile feedback is integrated into their experiences. This engagement leads to better retention of information and a more enjoyable interaction overall.
.
Adaptive Interactions: Advanced haptic technologies can adapt to user actions in real-time, providing personalized feedback that enhances engagement and satisfaction.
Accessibility and Inclusion
Support for Disabled Users: Haptic feedback serves as a crucial tool for individuals with visual or auditory impairments, offering them an alternative way to receive information through touch. This makes VR applications more accessible and inclusive.
Enhanced Training and Simulation
Realistic Training Scenarios: In professional training environments, such as medical simulations or industrial training, haptic feedback allows users to practice skills in a safe and controlled manner. This realism helps reinforce muscle memory and improves learning outcomes.
Feedback for Skill Development: The tactile responses provided by haptic devices can help users develop skills more effectively by simulating real-world interactions, such as flipping switches or manipulating tools.
Cognitive Load Reduction
Intuitive Interactions: Haptic feedback reduces cognitive load by providing additional sensory information that helps users navigate interfaces more intuitively. This allows for quicker responses and less reliance on visual or auditory cues alone.
Summary
In summary, haptic feedback significantly enhances the VR experience by improving realism, engagement, accessibility, training effectiveness, and user interaction. These benefits make it an essential component of modern virtual environments.
Sources
https://growthnatives.com/blogs/development/understanding-virtual-reality-and-augmented-reality/
https://nxtinteractive.ae/blog/the-latest-developments-in-ar-and-vr-technology
https://www.tdk.com/en/tech-mag/past-present-future-tech/ar-vr-mr
https://www.onirix.com/ar-vs-mr/
https://bernardmarr.com/the-important-difference-between-augmented-reality-and-mixed-reality/
https://ellow.io/what-is-haptic-feedback/
https://www.bairesdev.com/blog/your-app-needs-haptic-feedback/
https://elearningdesigncenter.com/benefits-of-haptic-feedback-in-the-virtual-world/












