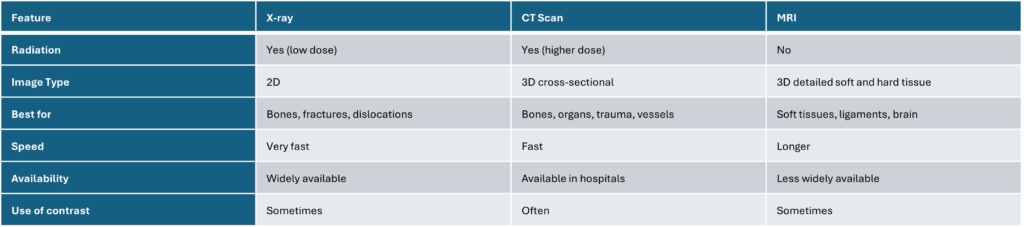
Here the overview of our THAUMATEC Blogposts inclusive the assignment to the Blogpost types
- HealthTech Industry Updates
- HealthTech Knowledge Guide
- IOT Technology and Experience
- Thaumatec
and inside HealthTech Industry Updates the HealthTech Industry Blogpost topics and domains
- HealthTech Trends and Reports
- MedTech Regulation Impact
- Telehealth
- Smart Digital Healthcare
- Smart Devices and Wearables
- Robots and AI for Health
to navigate better through the whole Data Base Blogpost material.
Most recent articles/posts are on the bottom of every chapter/block.
HEALTHTECH INDUSTRY UPDATES
HealthTech Trends and Reports
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/healthtech-industry-update-how-digital-fitness-is-changing-the-future-of-wellbeing/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/healthtech-industry-update-top-10-medical-device-companies-in-2022/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/growth-of-wearable-technology-in-healthcare-and-forecast-2023/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/healthtech-industry-update-where-it-leaders-should-focus-their-energies/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/major-healthcare-technology-trends-of-2022/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/healthtech-industry-update-why-healthtech-gets-our-pulses-racing/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/healthtech-industry-update-patients-report-better-telehealth-experiences-than-providers/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/healthtech-industry-update-digital-healthcare-trends-for-patient-treatment/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/healthtech-industry-update-wearable-technology-in-healthtech/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/knowledge-database-digital-technology-for-heart-health-care-and-monitoring-for-cardiac-patients/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/healttech-industry-update-top-medical-innovations-2023/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/healthtech-industry-update-healthcare-technology-trends-in-2023/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/healthtech-industry-update-femtech-innovation-on-postpartum-depression-ppd/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/healthtech-industry-update-what-women-want-out-of-their-health-benefits/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/healthtech-industry-update-health-tech-world-changes-in-2024-investor-outlook/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/healthtech-industry-update-medical-breakthroughs-of-2023/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/healthtech-industry-update-imaging-industry-trends-2023-and-2024-outlook/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/healthtech-industry-update-market-outlook-medical-technology-2024/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/healthtech-industry-update-embedded-systems-and-medical-devices-evolution-and-market/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/healthtech-industry-update-prioritizing-patient-care/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/thaumatec-healttech-industry-update-7-major-medtech-trends/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/healthtech-industry-update-3d-medical-device-manufacturing/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/thaumatec-industry-update-advances-in-stretchable-microelectronics-for-wearables-and-implants/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/thaumatec-healthtech-industry-update-aiot-artificial-intelligence-in-iot/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/thaumatec-healthtech-industry-update-technology-for-private-practices/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/thaumatec-healthtech-industry-update-how-startups-can-achieve-a-successful-tech-pilot/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/thaumatec-healthtech-industry-update-how-startups-can-achieve-a-successful-tech-pilot/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/thaumatec-healthtech-industry-update-a-way-to-green-hospitals/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/thaumatec-healthtech-industry-update-most-important-topics-in-healthcare-digital-health-and-medical-devices/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/healthtech-industry-update-overview-of-technical-advances-in-veterinary-medicine/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/thaumatec-healthtech-industry-update-advances-in-transportable-medical-devices-for-emergency-care-in-2025/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/thaumatec-healthtech-industry-update-digital-twin-in-medicine/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/thaumatec-healthtech-industry-update-healthtech-applications-and-devices-which-use-ar-vr-or-mr-technology/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/thaumatec-healthtech-industry-update-new-medtech-wearable-sensors-in-2025/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/thaumatec-healhtech-industry-update-hospitals-environmental-health-improvements-overview/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/thaumatec-industry-update-how-is-3d-printing-changing-healthcare-and-medical-devices/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/thaumatec-industry-update-how-does-3d-printing-allow-for-the-creation-of-bioabsorbable-implants/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/thaumatec-healthtech-industry-update-which-advances-and-innovations-are-expected-in-the-field-of-endoscopy/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/thaumatec-healthtech-industry-update-which-advances-are-expected-in-the-field-of-endoscopy-part3/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/thaumatec-healthtech-industry-update-what-are-the-differences-between-usa-and-eu-healthcare-systems/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/thaumatec-healthtech-industry-update-the-car-as-a-space-for-health/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/thaumatec-healthtech-industry-update-global-news-from-healthtech-digital-health-and-medical-devices/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/thaumatec-healthtech-industry-update-advances-in-dietetics-2025/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/thaumatec-healthtech-industry-update-advances-in-environmental-health-tech-in-2025/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/thaumatec-healthtech-industry-update-advances-in-mental-health-technology-in-2025/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/thaumatec-healthtech-industry-update-healthtech-advances-in-cancer-treatment/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/thaumatec-healthtech-industry-update-what-is-radiology-and-what-are-the-2025-advances/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/thaumatec-healthtech-industry-update-current-advances-on-hospital-food-catering-digital-menus-and-food-ordering-systems/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/thaumatec-healthtech-industry-update-medical-device-and-digital-health-highlights-in-april-and-mai-2025/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/thaumatec-healthtech-industry-update-important-europe-healthtech-events-in-june-2025/
MedTech Regulation Impact
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/healthtech-industry-update-engineering-excellence-in-highly-regulated-environments/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/healthtech-industry-update-how-to-stay-at-the-forefront-of-healthcare-innovation/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/healthtech-industry-update-in-vitro-diagnostics-device-ivd-regulation-implementation/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/healthtech-industry-update-from-the-idea-to-a-medical-device/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/healthtech-industry-update-access-and-diversity-in-clinical-trials/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/healthtech-knowledge-guide-service-oriented-device-connectivity-sdc/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/thaumatec-knowledge-guide-what-is-the-european-health-data-space-ehds/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/thaumatec-industry-update-which-digital-health-and-medical-device-innovations-are-expected-for-2025/
Telehealth
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/healthtech-industry-update-security-of-5g-enabled-internet-of-medical-things-iomt/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/healthtech-industry-update-how-virtual-reality-is-expanding-health-care/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/healthtech-industry-update-the-doctors-visit-of-the-future/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/healthtech-industry-update-multitasking-microneedle-sensor/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/healthtech-industry-update-telehealth-visits-lead-to-fewer-follow-up-visits-than-office-visits/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/healthtech-industry-update-medicine-delivered-by-drones-to-medical-deserts/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/thaumatec-healthtech-industry-update-first-extra-long-range-magnetic-tele-endoscopy/
Smart Digital Healthcare
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/healthtech-industry-update-high-tech-hospital-uses-artificial-intelligence-in-patient-care/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/healthtech-industry-update-carbon-neutral-green-hospital-2/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/healthtech-industry-update-how-to-reduce-the-attack-surface-for-healthcare-organisations/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/healthtech-industry-update-medical-imaging-technology-the-patient-impact/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/could-ai-shorten-hospital-wait-timeshealthtech-industry-update-could-ai-shorten-hospital-wait-times
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/healthtech-industry-update-from-post-it-notes-to-ai/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/healthtech-industry-update-medtech-integration-with-healthcare-workflows/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/healthtech-industry-update-new-framework-to-evaluate-digital-health-products
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/healthtech-industry-updated-better-data-quality-means-a-better-future-for-public-health/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/healthtech-industry-update-clinical-trials-have-a-data-problem/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/thaumatec-healthtech-industry-update-personalize-patient-care-with-confidence/
Smart Devices and Wearables
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/healthtech-industry-update-best-mental-health-apps-of-2023/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/healthtech-industry-update-7-top-patient-apps-in-ehealth/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/healthtech-industry-update-the-10-best-nutrition-apps-to-download/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/device-for-timely-diagnosis-of-alzheimer-disease/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/healthtech-industry-update-innovations-tackling-youth-mental-health-challenges/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/healthtech-industry-update-tool-to-spot-breast-cancer-at-home/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/healthtech-industry-update-medical-device-using-electrical-nerve-stimulation/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/healthtech-industry-update-protection-of-the-elderly-with-airbag-vests/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/emerging-technologies-for-diabetes-care/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/healthtech-industry-update-new-wearable-medical-sensors/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/healthtech-industry-update-ai-enhanced-ultrasound-for-womens-health/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/thaumatec-healthtech-industry-update-fda-qualifies-apple-watch/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/healthtech-industry-update-20-innovations-in-dentistry-that-will-shape-the-future/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/thaumatec-healthtech-industry-update-overview-and-thaumatec-blogpost-collection-of-smart-medical-devices-and-wearables-in-healthtech/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/thaumatec-healthtech-industry-update-endoscopic-devices-advances-trends-and-market/
Robots and AI for Health
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/healthtech-industry-update-magnetically-navigated-robots-to-attack-and-remove-blood-clots/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/healthtech-industry-update-will-robots-replace-surgeons/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/healthtech-industry-update-first-real-nanobots-entering-your-body/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/healthtech-industry-update-the-robot-surgeon-you-can-swallow/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/healthtech-industry-update-how-exoskeleton-technology-can-transform-healthcare/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/healthtech-industry-update-inside-the-lab-where-robots-run-their-own-experiments/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/healthtech-industry-update-ai-for-wireless-capsule-endoscopy/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/healthtech-industry-update-chatgpt-in-clinical-trials/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/healthtech-industry-update-machine-learning-prediction-model-for-inflammatory-bowel-disease/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/healthtech-industry-update-dignose-diseases-via-retinal-scans/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/healthtech-industry-update-can-ai-augment-empathy-and-compassion-in-healthcare/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/healthtech-industry-update-2024-the-year-of-health-tech/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/news/thaumatec-10th-anniversary/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/healthtech-industry-update-ai-in-healthcare-options-decisions-and-goals/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/thaumatec-healthtech-industry-update-artificial-intelligence-and-robotics-in-healthtech/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/healthtech-industry-update-are-healthcare-professionals-ready-for-ai/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/thaumatec-healthtech-industry-update-how-can-healthcare-ensure-responsible-ai-use/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/healthtech-industry-update-artificial-intelligence-in-the-medical-imaging-technology/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/thaumatec-healttech-industry-update-5-ways-ai-could-improve-the-world/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/thaumatec-healthtech-industry-update-hospitals-need-patient-trust-in-genai/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/thaumatec-healthtech-industry-update-clinical-documentation-ai-tools-in-health-care-systems/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/thaumatec-healthtech-industry-update-insights-at-the-point-of-care-and-beyond-using-ai/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/here-are-ways-that-robotics-are-transforming-the-medical-industry-thaumatec-healthtech-industry-update-how-robotics-will-transform-healthcarehere-are-ways-that-robotics-are-transforming-the-medical/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/thaumatec-healthtech-industry-update-the-evolution-of-clinical-practice-with-ai/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/thaumatec-healthtech-industry-update-robotics-in-surgery-2024/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/thaumatec-healthtech-industry-update-which-advances-on-surgeon-robots-are-expected-in-2025/
- https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/thaumatec-healthtech-industry-update-which-advances-are-expected-in-the-field-of-endoscopy-part2/
HEALTHTECH KNOWLEDGE GUIDE
https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/healthtech-knowledge-what-is-quadruple-aim/
https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/thaumatec-knowledge-guide-an-introduction-to-healthtech/
https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/5-things-you-need-to-know-about-wearable-medical-devices/
https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/knowledge-database-medical-reimbursement-in-eu/
https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/knowledge-database-biometrics-in-computer-vision-systems/
https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/healthtech-knowledge-guide-barrier-free-software/
https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/healthtech-knowledge-guide-digital-health-and-iomt/
https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/thaumatec-knowledge-guide-what-does-non-invasive-mean/
https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/thaumatec-knowledge-db-some-background-of-vr-ar-and-mr/
https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/thaumatech-healthtech-knowledge-guide-all-about-fhir/
https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/thaumatec-knowledge-db-emc-testing-of-medical-devices/
IOT TECHNOLOGY AND EXPERIENCE
https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/interview-with-pawel-adamek-qa-in-thaumatec-tech-group/
https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/different-radio-access-methods/
https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/bluetooth-low-energy-direction-finding/
https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/iot-and-the-importance-of-strategic-differentiation/
https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/iot-and-the-importance-of-operational-effectiveness/
https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/rustfest/
https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/a-classic-snake-game-in-rust/
https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/ignite-2019-reveals-new-azure-synapse/
https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/how-iot-will-change-in-the-upcoming-years/
https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/yocto-fundamentals/
https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/less-talked-about-but-still-great-rust-features/
https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/meet-thaumatec-during-cloudfest-in-germany/
https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/our-thoughts-on-ecs-2018/
https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/hawkish-on-risc-v/
https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/lwm2m-fundamentals/
https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/programming-atari/
https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/lora-distance-world-record-702-km/
https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/iot-connected-prototypes-overview-and-experience/
https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/technological-history-women-who-changed-the-tech-world/
THAUMATEC
https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/10-steps-to-successfully-start-international-cooperation/
https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/from-team-projects-conference-to-a-job-in-thaumatec/
https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/developers-dedicated-travel-agency/
https://thaumatec.com/knowledge/blog-posts/top-100-smartest-cities-in-the-world-wroclaw-ranks-in-95/